Because the modal fabric is not only soft but also environmentally friendly, it is a popular fabric choice among many people. European beech wood is beaten and spun into modal fiber. The raw material can naturally decompose and is entirely natural, and safe for use on humans and the environment.
The benefits and drawbacks of modal fabric will then be discussed.
Advantages of Modal Fabric
Natural wood is the source of modal fiber’s initial constituent, which can naturally deteriorate after use.
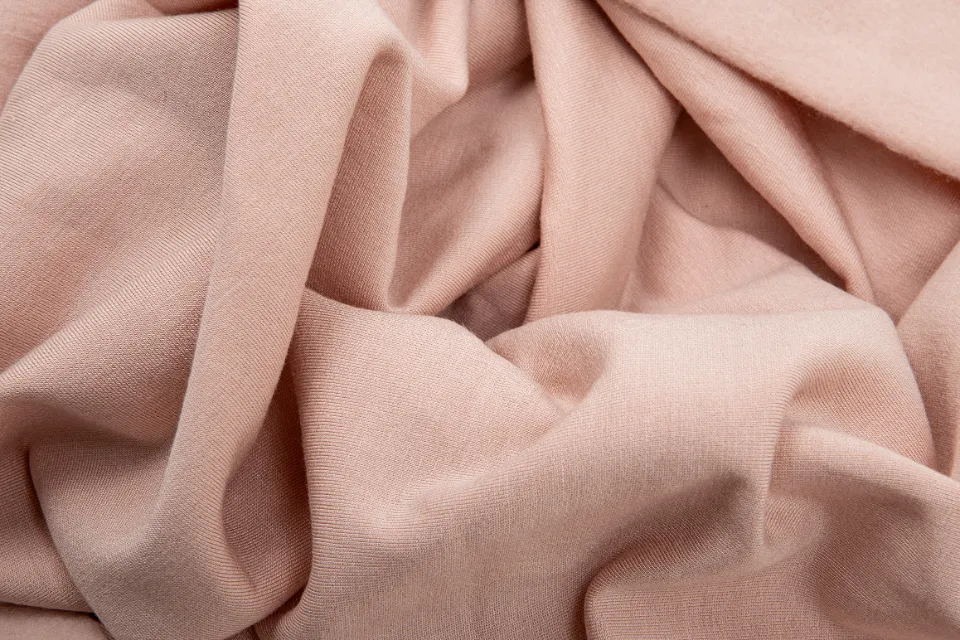

Soft, smooth, and colorful, modal fiber is. Compared to current cotton, polyester, and rayon fabrics, this one feels extremely smooth, has a bright luster, and is easier to drape. The fabric has a silky sheen and a natural mercerized finish.
With a dry strength of 35.6cm and a wet strength of 25.6 cm, which is higher than pure cotton and polyester cotton, modal fiber has the toughness and strength of synthetic fibers, minimizing the phenomenon of processing interruptions.
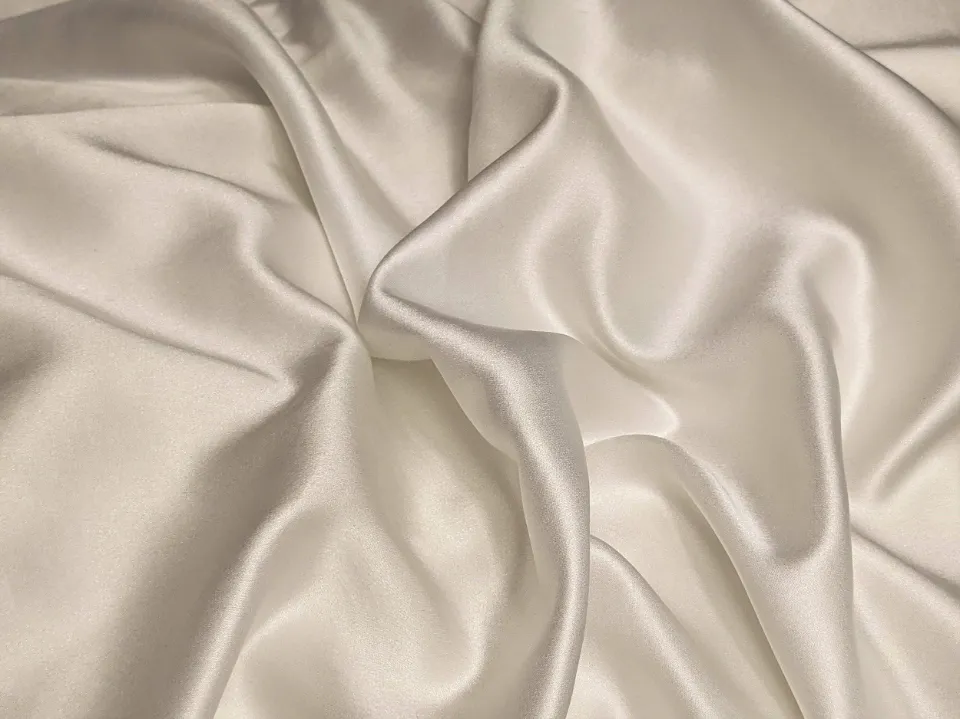

Modal fiber can absorb 50% more moisture than cotton fiber, making it ideal for making dry, breathable fabrics. It is a great fabric for tight clothing and bedding and is good for human physiological circulation and health.
Modal fiber, in comparison to the cotton fiber, has good shape and dimensional stability, giving the fabric a natural resistance to wrinkles and non-ironing qualities, making it more comfortable and natural to wear.

Modal fiber dyes extremely well, and even after numerous items of washing, it retains its original brilliance, comprehensive moisture absorption and good color fastness. Compared with pure cotton, it is more comfortable to wear, without the disadvantage of the easy fading and yellowing of pure cotton clothing. The fabric has a vibrant color and reliable wearing properties as a result. Here are the comparisons of Modal Fabric Vs Cotton.

Disadvantages of Modal Fabrics
Just because the modal fabric is relatively light and thin, its disadvantage is that it is easily shrunk. You should take extra care when cleaning these fabrics if you have any at home.
Generally speaking, to prevent deformation, this type of fabric shouldn’t be twisted tightly when it is washed, dried flat, or supported by hangers.
Given that modal is typically more expensive than pure cotton as a textile, you should make your purchase based on your individual needs.

What is Modal?
Modal is a new high wet modulus viscose fiber and a new generation of regenerated cellulose fiber. All-natural components, including European beech wood that has been first converted into wood pulp and then put through a unique spinning process, are used as the product’s raw materials.
Fibers are created by processing silk. Since more than 99% of the solvent used in the spinning process can be recycled, the entire production process produces virtually no pollution and is safe for human consumption, and can decompose naturally. It is environmentally friendly and is referred to as green. Eco-friendly fibers.

Conclusion
The development and utilization of modal fiber cater to people’s desire to “return to nature” and use natural fibers. The dry strength of Modal fiber is comparable to that of polyester, and its wet strength is significantly higher than that of regular viscose.
In comparison to products made of pure cotton, this fabric performs better in terms of gloss, softness, hygroscopicity, dyeability, and color fastness. It also has a silky sheen, a pleasantly soft touch, a smooth drape, and excellent durability. You can find more information about modal fabric in Display Cloths website!